A Tale of Two Tragedies: Trishuli Bus Accident vs. Saurya Airlines Flight Crash
Date and Location
Trishuli Bus Accident: July 12, 2024, Narayanghat-Mugling road, Chitwan
Saurya Airlines Flight Crash: July 24, 2024, Tribhuvan International Airport, Kathmandu
The Incidents
Trishuli Bus Accident
On July 12, 2024, two buses traveling on the Narayanghat-Mugling road were swept into the Trishuli River by a massive landslide. One bus was en route to Gaur, and the other to Kathmandu, carrying a total of 65 passengers. Rescue operations were severely hindered by continuous rain and the swollen river, complicating efforts to locate the buses. As of now, all 65 passengers are missing, with only three survivors who managed to swim to safety.
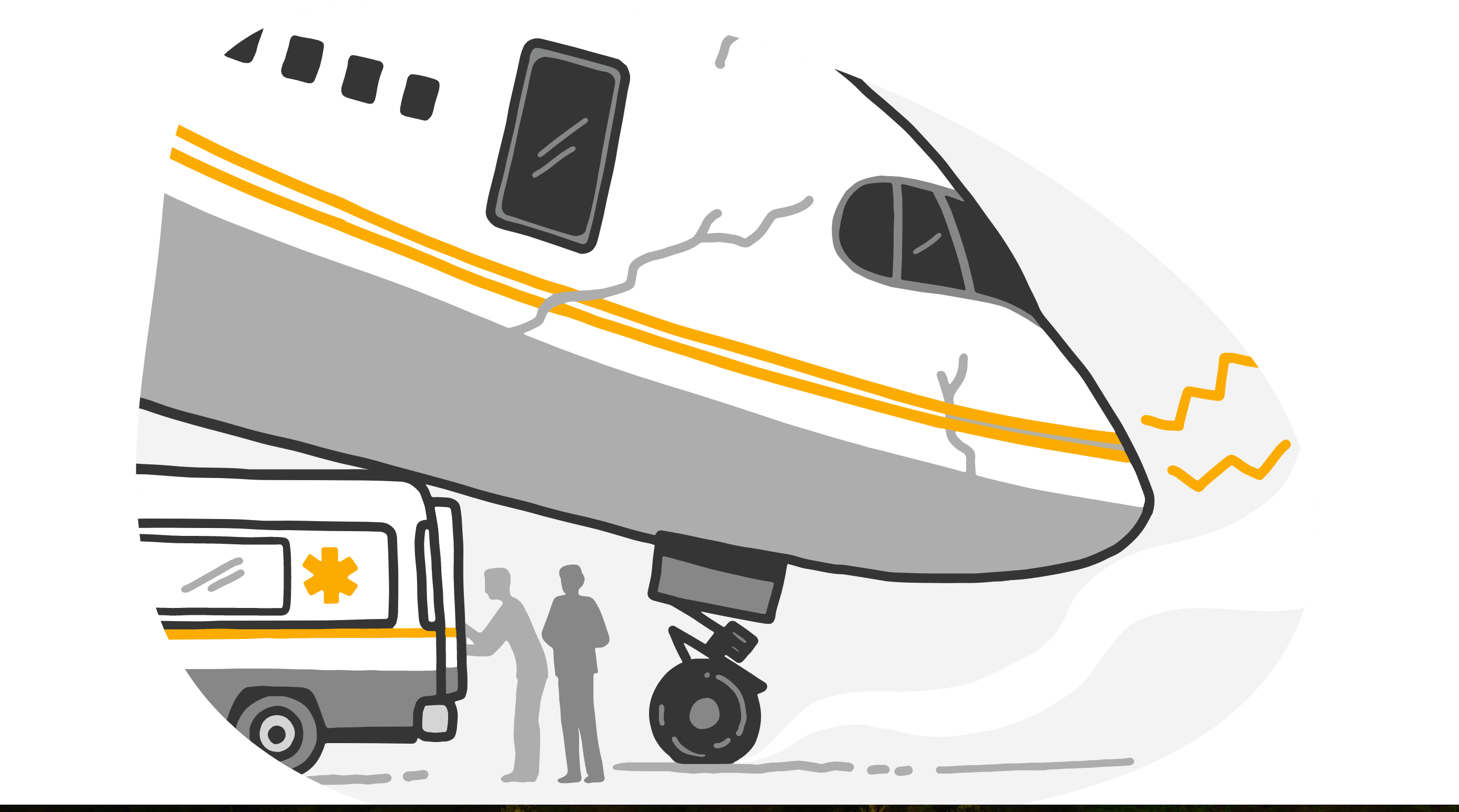
Saurya Airlines Flight Crash
On July 24, 2024, a Saurya Airlines flight crashed shortly after takeoff from Tribhuvan International Airport. The aircraft was on a routine test flight to Pokhara and had 19 people on board. The crash resulted in 18 fatalities, with the sole survivor being the pilot, Captain Manishratna Shakya, who sustained critical injuries and was immediately hospitalized.
Casualties and Survivors
Trishuli Bus Accident:
- Total Passengers: 65
- Survivors: 3
- Fatalities: 62 (presumed dead as the buses have not been found)
Saurya Airlines Flight Crash:
- Total Passengers: 19
- Survivors: 1
- Fatalities: 18
Government Response
Cabinet Decisions and Investigation Commission
The government did not form a Cabinet decision for an investigation commission for the Trishuli bus accident. In stark contrast, following the Saurya Airlines plane crash, the Nepalese Cabinet quickly established an investigation commission led by former CAAN Director General Rati Shakya, tasked with presenting a report within 45 days.
Prime Minister's Visit
Prime Minister KP Sharma Oli visited Captain Shakya, the sole survivor of the plane crash, to express his support and oversee the rescue and investigation efforts. However, no such visit was reported for the survivors or families of the victims of the Trishuli bus accident.
Socioeconomic Disparity
The differing government responses to these two tragedies might reflect underlying socioeconomic disparities. The bus accident likely involved poorer individuals, while the plane crash included more affluent passengers, potentially influencing the urgency and scale of the government’s reaction.
Comparative Analysis
-
Government Action:
- Bus Accident: No Cabinet decisions or investigation commission.
- Plane Crash: Cabinet formed an investigation commission, and immediate steps were taken.
-
Number of Victims:
- Bus Accident: 65 passengers, 62 presumed dead.
- Plane Crash: 19 passengers, 18 dead.
-
Prime Minister's Involvement:
- Bus Accident: No reported visit.
- Plane Crash: Prime Minister visited the survivor in the hospital.
-
Socioeconomic Factors:
- Bus Accident: Victims likely from lower socioeconomic backgrounds.
- Plane Crash: Victims included wealthier individuals, possibly influencing the robust governmental response.
Conclusion
The two tragic accidents—one involving a bus swept away by a landslide and the other a plane crash shortly after takeoff—highlight stark differences in governmental response and societal impact. While both incidents resulted in significant loss of life, the aftermath reveals potential biases in how such tragedies are managed, depending on the victims' socioeconomic status. The prompt establishment of an investigation commission and high-level visits following the plane crash contrast sharply with the more subdued response to the bus accident, underscoring the need for a more equitable approach to disaster management and victim support.




![From Kathmandu to the World: How Excel Students Are Winning Big [Admission Open]](https://nepalaaja.com/img/70194/medium/excel-college-info-eng-nep-2342.jpg)


